Sound Generation with AI
I started with music generation of MIDI files with Variational Auto Encoders some time ago. Check out the post here Music generation and learning Variational Autoencoders.
Then I found out about Encodec and Audiocraft. They are deep learning models for audio compression and sound generation. Audiocraft uses Encodec for the generation.

Encodec model

Audiocraft model
Encodec's paper is here: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.13438.pdf Audiocraft comprises two papers. MusicGen https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.05284.pdf and SoundGen https://arxiv.org/pdf/2209.15352.pdf.
I recommend reading both papers but beware that both papers are rabbit holes because they reference a whole lot of papers that themself reference a whole lot of paper. One paper I can really recommend is "Attention is all you need" https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf.
Here are the main parts of Encodec:
- Encoder: The encoder contains a list of convolutional blocks as well as a LSTM to reduce the dimensionality of the input while keeping the causality of the values.
- Quantizer: Encodec uses Residual Vector Quantization. The goal is to quantize the input into a discrete representation. RVQ is a vector quantization technique used in data compression. It involves encoding data by representing the difference (residual) between the original signal and a reconstructed version using quantized code vectors. Then you get a list of disctrete indexes instead of a continuous output.
- Decoder: The decoder is the inverse of the encoder.
- Discriminator: The discriminator is a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) that will try to predict which of the sounds is the original one and which is the decoded one.
- Losses: There are multiple losses in this model. *lw" is simply the difference between the RVQ input and output. ld and lg are the losses of the GAN. lt is the difference between input and output. Finally, ls is the difference between the mel spectrograms of the input and output at different scales. The mel spectrogram is similar to a FFT over time.
Here are the main parts of Audiocraft:
- Text encoder: A T5 pre-trained model to create embeddings from the text.
- Transformer: An autoregressive decoder transformer network with the text embeddings used as cross-attention. The transformer network will autoregressively generate discrete indexes of the RVQ. We can use these indexes to decode the audio with Encodec.
Anyway, I read all the papers and tried to understand the code which is opensource under MIT license https://github.com/facebookresearch/encodec and https://github.com/facebookresearch/audiocraft. However, the training is not provided and the trained weights on Hugging face have a more restrictive that prevents it from being used in commercial projects.
So I decided to write my own training code and make up my own dataset with public domain sounds. My goal is to make a tool that helps people generate sounds, either for video games, video editing or even music.
Below you can see an example of the current state of the app. I have been able to train Encodec well but Audiocraft is still struggling a bit. Facebook trained their model with 128 A100 GPUs for 200k steps (∼1 week). I don't really have that processing power unfortunately.
Demo of the app
First of all, I wrote a Python script to extract all of the https://freesound.org/ public domain audio files that I converted to mono 16'000 Hz.
Then I made a custom Google colab notebook where I used Pytorch to import the audio files, then import audiocraft and finally run the training. I used the V100 GPU on Google Colab which is not very expensive. I had to write some extra code for the training because not everything is provided with Audiocraft.
After training my own models I made a far too complicated architecture for my little prototype but it was very interesting to do.
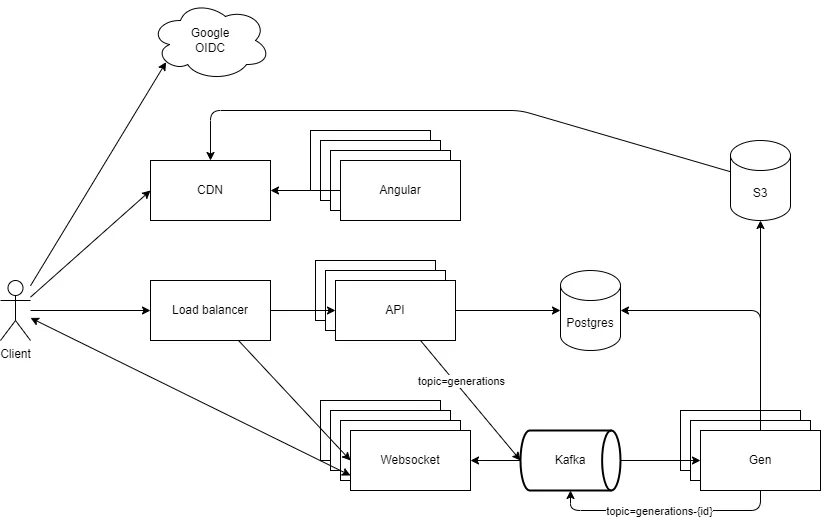
Architecture of the app
I'll break down the components quickly:
OpenID Connect (OIDC)
OIDC is an authentication layer on top of OAuth 2.0, an authorization framework. It allows applications to verify the identity of end-users based on the authentication performed by an authorization server. I use the Google authentication to authenticate the users. It is slightly more complicated than what happens in the diagram above.

OIDC architecture
Angular and CDN
The Angular application is built and then served through a Content Delivery Network (CDN). Using a CDN in front of a frontend has several advantages for web applications. A CDN is a network of servers distributed globally that work together to deliver content, such as images, stylesheets, scripts, and other assets, to users based on their geographical location. It improves the scalability, DDOS resistance and the data can be delivered faster.
API
The API is written with Apollo Server and GraphQL. GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that was developed by Facebook and released as an open-source project in 2015. It provides a more efficient, powerful, and flexible alternative to traditional REST APIs for fetching and updating data.
Postgres and S3
When triggering a new sound generation, we insert a row in the Generation table of the Postgres database. Then the file will be generated asynchronously (see below). When the file is created, it is pushed to the S3 storage and a reference to the file is inserted in the datbase.
Kafka and Gen
When the API receives a generation request, it will publish an event on a Kafka topic. The Gen application represents a consumer group that will take all the new events that come to the Kafka topic and start the sound generation using the Audiocraft pre-trained model.
Websocket
On the generation page, if the generation is not finished, the Angular application will connect to the Websocket server to try and get the status of the generation. The Websocket server consumes events from the Kafka status topic. Meanwhile the Gen application will push the status of the generations to that Kafka topic. This way the Angular app is able to get generation progress updates in real time.